Using such a framework facilitates deeper comprehension and encourages critical thinking skills. It helps viewers identify main ideas, supporting details, and underlying themes. This focused approach promotes retention of information and allows viewers to connect concepts presented in the video to broader knowledge. Furthermore, it provides a valuable tool for discussion and collaborative learning, as viewers can share their observations and interpretations based on a common structure.
This article further explores the creation and effective utilization of these valuable learning tools. Topics include best practices for design, specific examples for various video genres, and tips for integrating them into diverse learning environments.
Key Components of a Viewing Guide
Effective viewing guides incorporate several key components to maximize comprehension and engagement with video content. These components work together to provide a structured approach to viewing, encouraging active learning and deeper analysis.
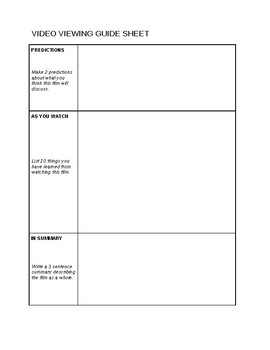
1: Pre-viewing Activities: These activities prepare viewers for the content by activating prior knowledge and establishing learning objectives. Examples include brainstorming questions, reviewing relevant vocabulary, or making predictions about the video’s message.
2: Focus Questions During Viewing: Specific questions guide viewers’ attention to crucial details within the video. These questions can target main ideas, supporting evidence, or specific visual elements.
3: Space for Note-Taking: Designated areas for note-taking allow viewers to record key observations, reflections, and answers to focus questions. This encourages active listening and provides a record for later review.
4: Post-viewing Activities: These activities facilitate deeper processing of the video’s content. Examples include summarizing key takeaways, analyzing perspectives presented, or connecting the video to other learning materials.
5: Vocabulary Clarification: A section dedicated to defining key terms ensures comprehension and provides an opportunity for vocabulary development. This is particularly helpful for videos containing specialized terminology.
6: Reflection Prompts: Open-ended questions encourage viewers to reflect on the video’s message and its implications. These prompts can explore personal connections, ethical considerations, or potential applications of the information presented.
A well-designed viewing guide provides a framework for active engagement, promotes deeper understanding, and facilitates meaningful reflection on video content, ultimately transforming passive viewing into an active learning experience.
How to Create a Video Viewing Guide
Creating a structured guide enhances comprehension and engagement with video content. The following steps outline a practical approach to developing effective viewing guides for various educational and professional purposes.
1: Define Learning Objectives: Clearly articulate the specific goals viewers should achieve after engaging with the video and guide. This focuses the design process and ensures alignment between content and objectives.
2: Analyze the Video Content: Thoroughly review the video to identify key concepts, supporting details, and potential challenges for viewers. This analysis informs the selection of appropriate pre-viewing, during-viewing, and post-viewing activities.
3: Develop Pre-Viewing Activities: Design activities that activate prior knowledge, introduce key vocabulary, and generate interest in the video’s topic. Examples include brainstorming questions, short quizzes, or brief discussions.
4: Formulate Focus Questions: Craft specific questions that guide viewers’ attention to crucial information during the video. These questions should target main ideas, supporting evidence, and critical analysis of the content.
5: Design Post-Viewing Activities: Develop activities that encourage reflection, discussion, and application of learned concepts. Examples include summarizing key takeaways, analyzing different perspectives, or connecting the video to real-world scenarios.
6: Incorporate Interactive Elements: Consider including interactive elements such as polls, quizzes, or discussion prompts to enhance engagement and facilitate active learning. These elements provide opportunities for immediate feedback and encourage participation.
7: Structure the Guide Clearly: Organize the guide logically with clear headings, subheadings, and designated spaces for note-taking. A well-structured guide facilitates easy navigation and promotes a positive user experience.
8: Test and Refine: Pilot test the guide with a small group of viewers and gather feedback to identify areas for improvement. Revisions based on feedback ensure clarity, effectiveness, and overall quality.
A thoughtfully designed guide transforms passive viewing into an active learning experience, promoting deeper understanding, critical thinking, and meaningful engagement with video content.
Structured frameworks for video engagement offer significant advantages for maximizing learning outcomes. From pre-viewing preparation to post-viewing reflection, a well-designed framework provides a roadmap for viewers to actively engage with content, extract key information, and develop critical thinking skills. The incorporation of focused questions, designated spaces for note-taking, and interactive elements further enhances comprehension and retention. Careful consideration of learning objectives, thorough content analysis, and iterative refinement processes are essential for creating effective frameworks tailored to specific educational and professional needs.
Effective utilization of these frameworks represents a shift from passive consumption to active engagement with video content. This approach fosters deeper understanding, encourages critical analysis, and promotes meaningful application of learned concepts. As video continues to play an increasingly prominent role in education and professional development, the strategic implementation of these frameworks becomes crucial for unlocking the full potential of video as a powerful learning tool.