Standardized documentation enhances efficiency by reducing time spent on repetitive tasks and troubleshooting common issues. It also facilitates knowledge transfer, enabling smoother onboarding of new personnel and minimizing disruption in the event of staff changes. Furthermore, a well-maintained framework strengthens operational security by ensuring adherence to established protocols and minimizing the risk of human error. Finally, such structure provides a valuable resource for auditing and compliance reporting.
The following sections will delve into the core components of a robust framework for managing IT infrastructure, including specific examples and practical implementation guidelines.
Key Components of a System Administration Framework
A comprehensive framework for system administration requires several key components to ensure its effectiveness and utility.
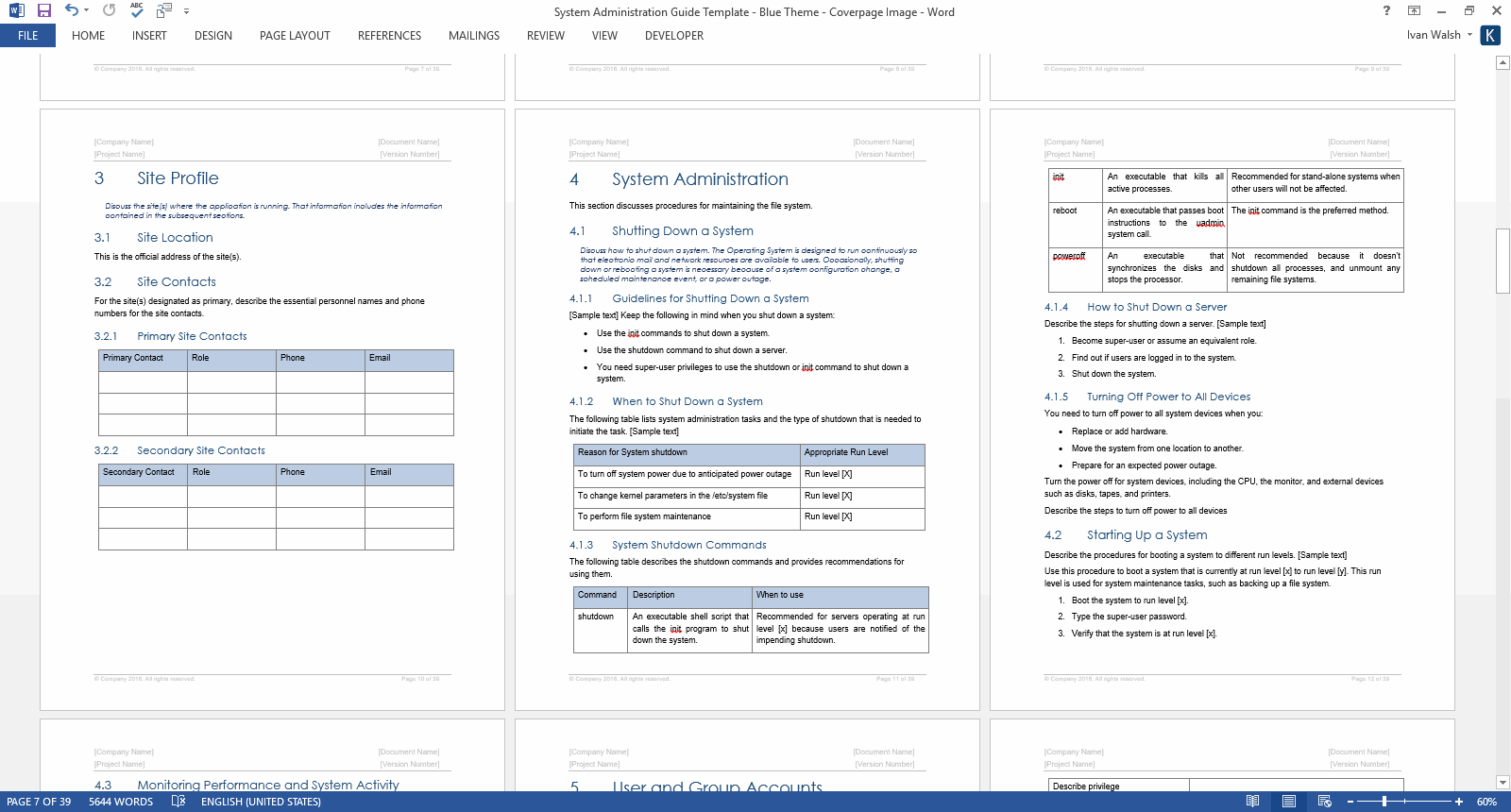
1: Account Management Procedures: This section details the processes for creating, modifying, and deleting user accounts, including password policies, access controls, and group management. Clear guidelines in this area are crucial for maintaining system security and regulatory compliance.
2: Security Protocols: Documentation of security measures, such as firewall rules, intrusion detection systems, and vulnerability scanning procedures, is essential. This section should also outline incident response plans and data recovery procedures.
3: Backup and Recovery Procedures: Detailed instructions for regular data backups, restoration processes, and disaster recovery scenarios are critical for business continuity. This component should specify backup frequencies, storage locations, and recovery time objectives.
4: System Configuration Standards: Consistent system configurations improve stability and manageability. This section should define standard operating system settings, software installations, and hardware specifications.
5: Performance Monitoring and Optimization: Guidelines for monitoring system performance, identifying bottlenecks, and implementing optimization strategies are necessary for maintaining optimal system responsiveness and resource utilization.
6: Change Management Processes: A structured approach to implementing system changes minimizes risks and disruptions. This component should outline procedures for requesting, approving, testing, and deploying changes.
7: Troubleshooting Guides: A collection of troubleshooting steps for common issues provides a valuable resource for resolving problems quickly and efficiently. This section should include diagnostic procedures and solutions for various error conditions.
8: Software and Hardware Inventory: Maintaining an up-to-date inventory of software and hardware assets is crucial for effective management and license compliance. This section should include details on software versions, hardware specifications, and warranty information.
Adherence to these components ensures a well-structured and effective framework, promoting efficient operations, robust security, and business continuity.
How to Create a System Administration Guide Template
Creating a robust template ensures consistent documentation and streamlines administrative tasks. The following steps outline a practical approach to developing such a template.
1: Define Scope and Audience: Clearly outline the systems and processes covered by the guide. Specify the intended audience (e.g., junior administrators, senior engineers) to tailor content and technical depth.
2: Establish a Standardized Structure: Utilize a consistent format with headings, subheadings, and numbered lists for easy navigation. Employ a clear and concise writing style, avoiding technical jargon where possible.
3: Develop Account Management Procedures: Document procedures for user account creation, modification, deletion, password resets, and access control management. Include relevant security policies and compliance regulations.
4: Outline Security Protocols: Detail firewall configurations, intrusion detection/prevention systems, vulnerability scanning procedures, and incident response plans. Address data encryption and access control methodologies.
5: Detail Backup and Recovery Procedures: Specify backup schedules, storage locations, restoration methods, and disaster recovery plans. Include instructions for verifying backup integrity and recovery testing.
6: Define System Configuration Standards: Document standard operating system settings, software installations, hardware specifications, and networking configurations. Ensure consistency across all managed systems.
7: Establish Change Management Processes: Outline procedures for requesting, approving, implementing, and documenting system changes. Include rollback plans and communication protocols.
8: Develop Troubleshooting Guides: Provide step-by-step instructions for diagnosing and resolving common issues. Include error codes, potential causes, and recommended solutions. Incorporate diagnostic tools and log analysis techniques.
A well-defined structure, comprehensive content, and regular updates are essential for maintaining a valuable and effective resource. Version control mechanisms should be implemented to track revisions and ensure accessibility to the most current information.
A robust system administration guide template provides a crucial foundation for consistent, efficient, and secure IT operations. By standardizing procedures, centralizing knowledge, and facilitating communication, such a framework empowers organizations to manage complex infrastructures effectively. Methodical documentation of account management, security protocols, backup/recovery procedures, system configurations, performance monitoring, change management, and troubleshooting processes contributes to enhanced stability, reduced downtime, and improved security posture.
Investing in the development and maintenance of a comprehensive system administration guide template represents a commitment to operational excellence and long-term success. This proactive approach mitigates risk, streamlines workflows, and empowers IT teams to deliver reliable and secure services, ultimately contributing to the overall stability and growth of an organization. Regular review and adaptation of this framework are essential to accommodate evolving technological landscapes and maintain alignment with best practices.