Utilization of such devices leads to improved implant positioning, optimized aesthetics, and reduced risk of complications. This precision contributes to better long-term outcomes, increased patient satisfaction, and a more efficient surgical process. Reduced chair time and improved prosthetic integration are also notable advantages.
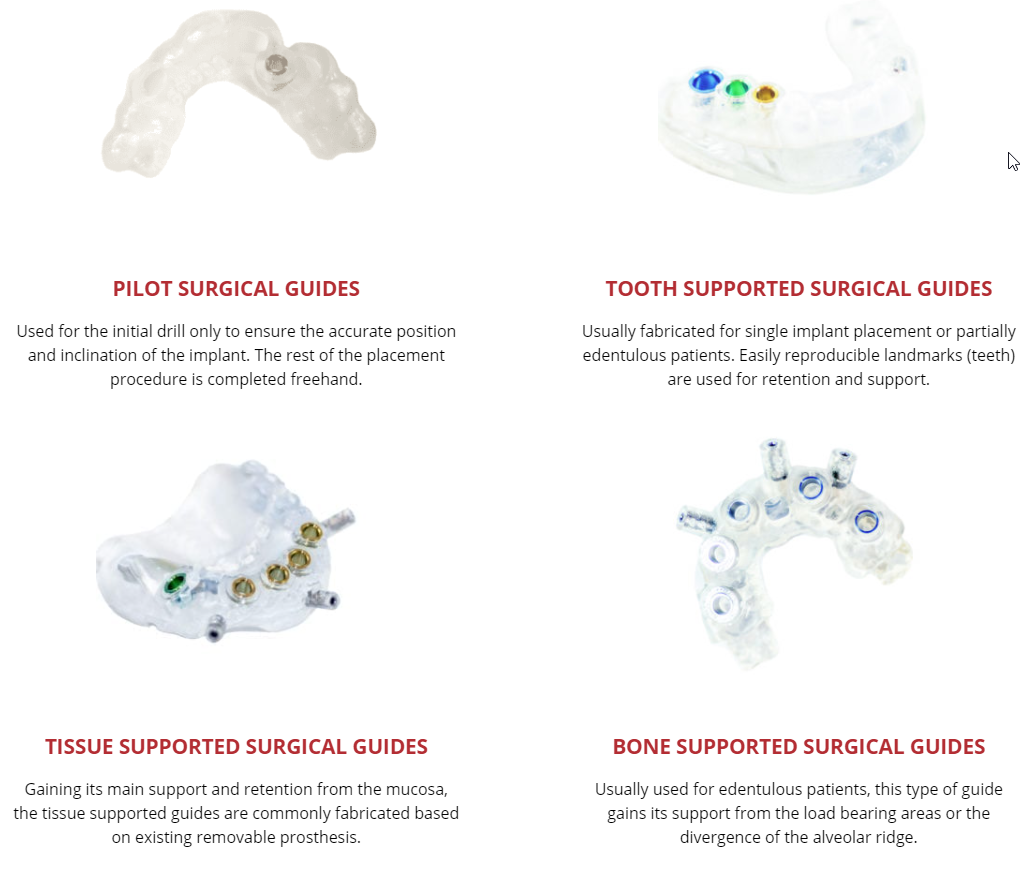
The following sections will delve deeper into the creation, application, and various types of these vital surgical tools, exploring their impact on contemporary implant dentistry.
Key Components of a Surgical Guide for Implants
A surgical guide for implant placement comprises several crucial components working in concert to ensure predictable and accurate outcomes.
1. Guide Body: The primary structure of the guide, typically fabricated from biocompatible materials like acrylic resin or similar polymers. This provides stability and dictates the placement trajectory.
2. Sleeves or Drill Guides: Metal or polymer cylinders embedded within the guide body. These constrain the drills to a predetermined path, controlling angulation and depth of implant osteotomy.
3. Stabilization Features: Elements that secure the guide to the patient’s existing dentition or bone structure during surgery. These may include fixation pins, resting surfaces on adjacent teeth, or mucosal support.
4. Implant Site Markings: Indicate the precise location and angulation of planned implants, sometimes featuring markings for different implant diameters.
5. Soft Tissue Management Design: Features incorporated into the guide to gently displace or protect soft tissues during the procedure, contributing to a less invasive approach.
6. Occlusal Stops/Clearance: Specific design elements that ensure adequate space for the final restoration and proper occlusal function.
Precise fabrication and accurate representation of the patient’s anatomy are paramount for effective use. Each element contributes to a predictable and efficient surgical workflow, ultimately promoting successful implant integration and prosthetic rehabilitation.
How to Create a Surgical Guide for Implants
Creation of a surgical guide involves a multi-stage process requiring precise planning and execution. A thorough understanding of each step is crucial for achieving optimal outcomes.
1: Data Acquisition: The process begins with acquiring comprehensive patient data. This typically involves a cone beam computed tomography (CBCT) scan to capture the three-dimensional anatomy of the jawbone and surrounding structures. Intraoral scans or impressions may also be used to capture the soft tissue and existing dentition.
2: Treatment Planning: Using specialized software, the implant placement is virtually planned based on the acquired data. Factors such as bone density, anatomical limitations, and prosthetic requirements are considered during this stage.
3: Guide Design: Once the virtual plan is finalized, the surgical guide is designed within the software. This involves defining the guide’s shape, position, and the precise location and angulation of drill sleeves. Considerations for soft tissue management and stabilization are also incorporated.
4: Guide Fabrication: The designed guide is then fabricated using various techniques, such as 3D printing or milling. Material selection is critical to ensure biocompatibility, rigidity, and accuracy.
5: Guide Verification (Optional but recommended): Before clinical use, the guide can be verified on a model created from the patient’s data. This step helps ensure proper fit and confirms the planned implant positions.
6: Sterilization: Prior to surgery, the guide must undergo appropriate sterilization procedures according to manufacturer guidelines and established infection control protocols.
Successful creation relies on accurate data acquisition, meticulous planning, and precise fabrication. Each stage contributes to the final precision and efficacy of the guide during implant placement surgery.
Precise implant placement is paramount for successful osseointegration and long-term functional and aesthetic outcomes. Surgical guides offer a reliable method to transfer virtual treatment plans to the surgical field, enhancing accuracy, predictability, and efficiency. From initial data acquisition and planning to guide fabrication and surgical application, a meticulous approach is crucial for maximizing the benefits of this technology. Understanding the components and fabrication process allows clinicians to harness the full potential of these tools, ultimately leading to improved patient care and more predictable results in implant dentistry.
As technology continues to advance, further refinements in surgical guide design and fabrication are anticipated, promising even greater precision and minimally invasive procedures. The ongoing development of these tools reinforces their vital role in modern implant dentistry, paving the way for more predictable, efficient, and patient-centric treatments.



