Utilizing such a framework offers numerous advantages. It promotes standardization across projects, leading to improved predictability and efficiency. Clear guidelines and predefined structures help teams stay organized, reducing ambiguity and the likelihood of errors. This, in turn, can lead to better resource allocation, improved stakeholder satisfaction, and ultimately, greater project success rates. A well-defined structure also facilitates knowledge transfer and onboarding of new team members.
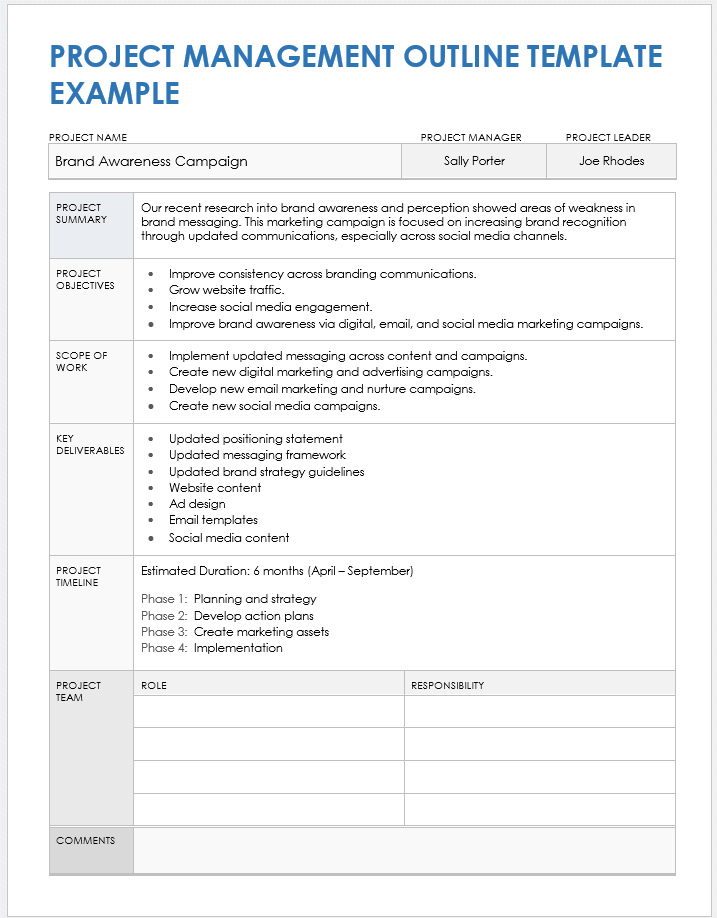
This foundational understanding of structured project frameworks paves the way for a deeper exploration of key components, including project initiation, planning, execution, monitoring and controlling, and closure. Each stage plays a vital role in overall project success and will be examined in detail.
Key Components of a Project Management Framework
Effective project management relies on a well-defined structure. The following components are crucial for establishing a robust framework and ensuring successful project outcomes.
1: Project Initiation: This stage defines the project’s purpose, objectives, and high-level scope. It involves identifying key stakeholders, establishing initial communication channels, and securing necessary approvals to proceed.
2: Project Planning: Detailed plans are developed during this phase, outlining specific tasks, dependencies, timelines, resource allocation, and budget. Risk assessment and mitigation strategies are also defined.
3: Project Execution: This phase involves carrying out the planned tasks, managing resources, and coordinating team efforts. Regular progress tracking and communication are essential for maintaining momentum and addressing any deviations from the plan.
4: Project Monitoring and Controlling: Performance is monitored against the established baseline. Corrective actions are taken to address variances, manage risks, and ensure the project stays on track in terms of scope, schedule, and budget.
5: Project Closure: This final stage involves formally closing the project, documenting lessons learned, archiving project deliverables, and celebrating accomplishments. Final reports are generated and shared with stakeholders.
A comprehensive framework, incorporating these key components, provides the structure and guidance necessary for navigating the complexities of any project, leading to increased efficiency, improved communication, and a higher likelihood of achieving desired outcomes. This structured approach promotes better risk management and ultimately contributes to greater project success.
How to Create a Project Management Guide Template
Creating a robust template facilitates consistent project management practices and improves the likelihood of successful outcomes. The following steps outline a structured approach to developing such a template.
1: Define Scope and Objectives: Clearly articulate the purpose and intended use of the template. Specify the types of projects it will support and the overall objectives it aims to achieve.
2: Structure the Template: Organize the template into logical sections, mirroring the key phases of the project lifecycle: initiation, planning, execution, monitoring and controlling, and closure. This structure ensures comprehensive coverage of all essential aspects.
3: Develop Content for Each Section: Populate each section with relevant details, guidelines, and prompts. Include sections for defining project scope, objectives, deliverables, timelines, resource allocation, risk management, communication plans, and reporting requirements.
4: Incorporate Best Practices: Integrate industry best practices and methodologies relevant to the target projects. Consider including templates for common project management documents, such as risk registers, communication plans, and progress reports.
5: Design for Usability: Ensure the template is user-friendly and easy to navigate. Use clear headings, concise language, and visual aids to enhance clarity and accessibility. Consider providing instructions or examples to guide users.
6: Test and Refine: Pilot test the template with a representative group of users to gather feedback and identify areas for improvement. Iteratively refine the template based on user feedback and practical application.
7: Implement and Train: Roll out the template across the organization and provide training to ensure consistent application. Establish a process for ongoing maintenance and updates to keep the template current and relevant.
A well-designed template provides a standardized framework, promoting consistency and efficiency in project management practices. This structured approach contributes to improved communication, better risk management, and ultimately, increased project success rates. Regular review and refinement of the template ensure its continued effectiveness and relevance within the evolving project landscape.
Standardized frameworks for managing projects, offering predefined structures for planning, execution, and closure, are essential for achieving consistent results. These frameworks provide a roadmap encompassing key components such as project initiation, planning, execution, monitoring and controlling, and closure. Each component contributes to a structured approach, promoting clarity, organization, and effective communication throughout the project lifecycle. Utilizing such frameworks leads to improved predictability, better resource allocation, and enhanced stakeholder satisfaction. Investing in well-designed frameworks empowers organizations to navigate project complexities effectively and achieve desired outcomes consistently.
Ultimately, the adoption and adaptation of structured project management methodologies represent a commitment to continuous improvement. Organizations that embrace these principles position themselves for greater success in an increasingly complex and competitive environment. The consistent application of robust frameworks fosters a culture of proactive planning, effective execution, and data-driven decision-making, leading to improved project outcomes and enhanced organizational performance.