Utilizing such a framework facilitates active recall, improves comprehension, and aids in applying theoretical knowledge to practical scenarios. It promotes a deeper understanding of drug interactions, therapeutic applications, and patient-specific considerations. This organized approach can significantly enhance exam preparation and contribute to long-term professional success.
The following sections will delve into specific components and offer practical strategies for developing and implementing an effective learning plan for pharmacology.
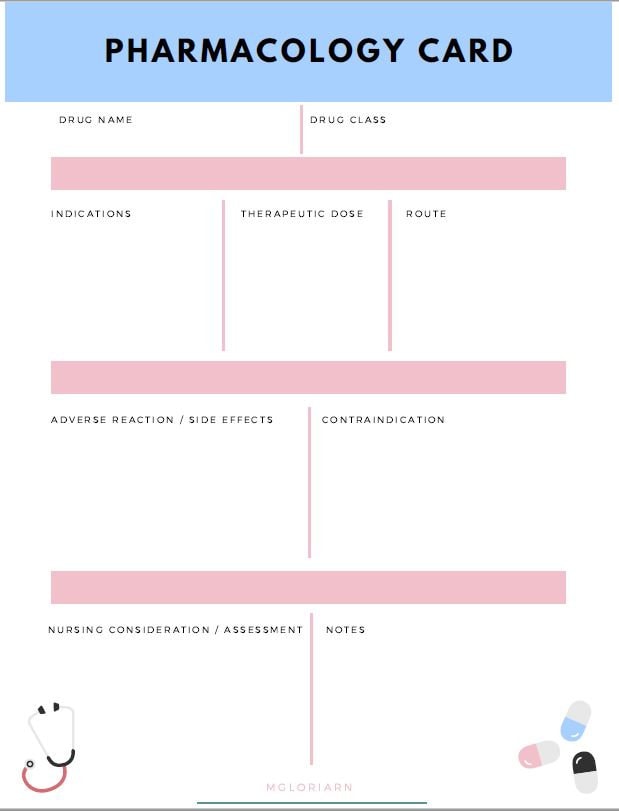
Key Components of a Pharmacology Study Resource
Effective resources for pharmacology study typically incorporate several key components to facilitate comprehensive learning and knowledge retention. These components provide a structured approach to mastering complex concepts and their practical applications.
1. Drug Classifications: A systematic organization of drugs based on their therapeutic use, mechanism of action, or chemical structure provides a foundation for understanding their effects. This includes exploring major drug classes like analgesics, antihypertensives, and antibiotics.
2. Mechanisms of Action: Detailed explanations of how drugs interact with the body at a molecular level are crucial. This encompasses receptor binding, signal transduction pathways, and subsequent physiological responses.
3. Pharmacokinetics: This component explores the processes of drug absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion (ADME). Understanding these processes is essential for predicting drug concentrations and optimizing dosing regimens.
4. Pharmacodynamics: This section focuses on the biochemical and physiological effects of drugs on the body. It examines dose-response relationships, drug efficacy, and therapeutic indices.
5. Adverse Effects and Drug Interactions: A thorough understanding of potential adverse effects and drug interactions is crucial for safe and effective drug administration. This component should detail common side effects, contraindications, and potential interactions with other medications or substances.
6. Clinical Applications and Therapeutic Uses: Linking pharmacological principles to real-world clinical scenarios is essential for practical application. This involves exploring specific therapeutic uses of drugs in various disease states and patient populations.
7. Review Questions and Practice Cases: Incorporating review questions, practice cases, and other active learning strategies reinforces understanding and prepares students for examinations and clinical practice. This allows for application of learned concepts and identification of areas requiring further study.
A well-structured resource incorporating these elements provides a robust framework for mastering complex pharmacological principles and applying them effectively in clinical practice. This facilitates a deeper understanding of drug actions, therapeutic applications, and patient-specific considerations.
How to Create a Pharmacology Study Guide
Developing a structured study guide facilitates effective learning and retention of complex pharmacological principles. A systematic approach ensures comprehensive coverage of essential concepts and their clinical applications.
1. Define Scope and Objectives: Clearly define the scope of the study guide based on specific learning objectives. Consider the course syllabus, learning outcomes, and professional goals.
2. Choose a Format: Select a format suitable for individual learning preferences. Options include digital documents, handwritten notes, flashcards, or a combination of methods.
3. Organize by Drug Class or Body System: Structure the guide either by drug class (e.g., analgesics, antihypertensives) or by body system (e.g., cardiovascular, respiratory). This provides a logical framework for information organization.
4. Include Key Information for Each Drug: For each drug, include essential information such as mechanism of action, pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics, therapeutic uses, adverse effects, and drug interactions.
5. Incorporate Visual Aids: Utilize diagrams, flowcharts, and other visual aids to enhance understanding and memory retention of complex processes.
6. Summarize Key Concepts: Condense complex information into concise summaries to facilitate quick review and reinforce key takeaways.
7. Include Practice Questions and Case Studies: Integrate practice questions, case studies, and clinical scenarios to apply knowledge and identify areas requiring further study.
8. Regularly Review and Update: Periodically review and update the study guide to reflect new knowledge and reinforce learned concepts.
A well-structured guide, tailored to individual needs and regularly reviewed, promotes comprehensive understanding and facilitates application of pharmacological principles in clinical practice.
A well-defined framework for organizing pharmacological knowledge provides a crucial tool for effective learning and application in professional practice. Such a resource, incorporating key drug information, mechanisms of action, pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics, adverse effects, and clinical applications, offers a structured approach to mastering this complex field. Developing and utilizing such a resource contributes significantly to improved comprehension, retention, and application of pharmacological principles.
Mastery of pharmacological principles remains essential for safe and effective medication management. Continuous engagement with evolving knowledge in this dynamic field equips healthcare professionals to provide optimal patient care and contribute to advancements in therapeutic interventions.