Utilizing such a structure facilitates active listening, encourages critical thinking about musical elements, and promotes a more enriching engagement with music. It allows for structured note-taking, comparative analysis, and the development of a richer musical vocabulary. This can be particularly valuable for educational settings, self-directed learning, or simply enhancing personal listening experiences.
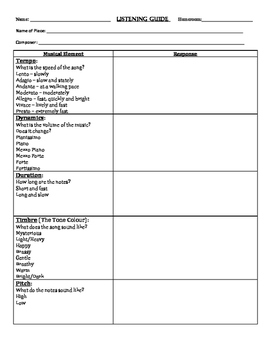
This foundational understanding of structured listening frameworks allows for a more meaningful exploration of specific applications and benefits. Topics such as template design, adaptation for diverse musical styles, and integration into educational curricula are explored further in the following sections.
Key Components of a Structured Listening Framework
Effective frameworks for enhanced musical comprehension typically incorporate several key elements. These components work together to provide a comprehensive approach to active listening and analysis.
1: Basic Information: This section typically includes the title, composer, performer, and date of composition. Contextual details such as the musical period or genre can also be included.
2: Initial Impressions: A space for recording first impressions of the piece. This encourages immediate emotional responses and subjective interpretations.
3: Melodic Elements: Prompts to analyze the melody. Are there recurring themes or motifs? Is the melody conjunct or disjunct? How does the melody contribute to the overall mood?
4: Rhythmic Elements: This section focuses on the rhythmic structure. Is the rhythm regular or irregular? Are there syncopations or polyrhythms? How does the rhythm contribute to the energy of the piece?
5: Harmonic Elements: Analysis of the harmony and chord progressions. Are the harmonies consonant or dissonant? How do the harmonies contribute to the overall emotional impact?
6: Timbre and Texture: Exploration of the instruments or voices used and how they interact. Is the texture monophonic, homophonic, or polyphonic? How does the timbre contribute to the overall sound world?
7: Form and Structure: Analysis of the overall structure of the piece. Is it in binary form, ternary form, or sonata form? How does the structure contribute to the listener’s experience?
8: Personal Reflection: A space for final thoughts and reflections after a more focused listening experience. This allows for a deeper engagement with the music and encourages personal connections.
Through the careful consideration of these elements, a richer and more informed understanding of music can be achieved. These individual components provide a framework for focused listening, allowing both novice and experienced listeners to develop a deeper appreciation for the complexities and nuances of musical works.
How to Create a Music Listening Guide Template
Creating a structured template facilitates focused listening and deeper musical analysis. The following steps outline the development of a versatile template adaptable for diverse musical genres and educational contexts.
1: Define the Scope: Determine the intended purpose and target audience. A template for elementary students will differ significantly from one designed for university music analysis. Specifying the scope ensures relevance and practicality.
2: Select Essential Elements: Choose components relevant to the defined scope. Basic information (composer, title, etc.) is typically included, while more advanced elements (harmonic analysis, form) may be added based on the target audience’s musical knowledge.
3: Structure the Template: Organize the chosen elements logically. A clear, sequential structure facilitates focused listening and systematic analysis. Consider using headings and subheadings to delineate sections.
4: Develop Guiding Questions: Formulate open-ended questions within each section to prompt critical thinking. Questions should encourage active listening and deeper engagement with the musical elements.
5: Incorporate Visual Aids: Where appropriate, include visual aids such as staff notation, diagrams, or images. Visual elements can enhance understanding, particularly for complex musical concepts.
6: Test and Refine: Utilize the template with representative musical examples to assess its effectiveness. Revise and refine the template based on feedback and practical application. This iterative process ensures clarity and functionality.
A well-designed template provides a structured approach to musical analysis, promoting active listening and deeper engagement with musical works. Adaptability and relevance to the intended audience are crucial for maximizing the template’s effectiveness as an educational and analytical tool.
Structured frameworks for listening offer a valuable method for engaging with music on a deeper level. From basic identification of musical elements to more nuanced analysis of form and structure, these templates provide a roadmap for focused listening. The adaptability of these frameworks allows for application across diverse genres, historical periods, and educational levels, fostering a more enriching musical experience.
Cultivating active listening skills through structured approaches ultimately enhances musical appreciation and understanding. The utilization of these templates represents an investment in developing a more profound connection with music, fostering lifelong learning and a greater appreciation for the complexities of musical expression.