A structured framework for organizing one’s assets and wishes for their distribution after death is essential for a smooth transition and minimizing potential conflicts. This framework typically provides a step-by-step approach to documenting key decisions, including beneficiary designations, asset allocation, and healthcare directives. It offers a standardized format for compiling crucial information, simplifying the complex process of estate administration.
Utilizing such a framework offers numerous advantages. It provides clarity and direction, ensuring wishes are documented accurately and comprehensively. This proactive approach can minimize the burden on loved ones during a difficult time, reducing stress and potential disputes. Furthermore, it allows individuals to maintain control over their assets and legacy, providing peace of mind and ensuring their intentions are respected.
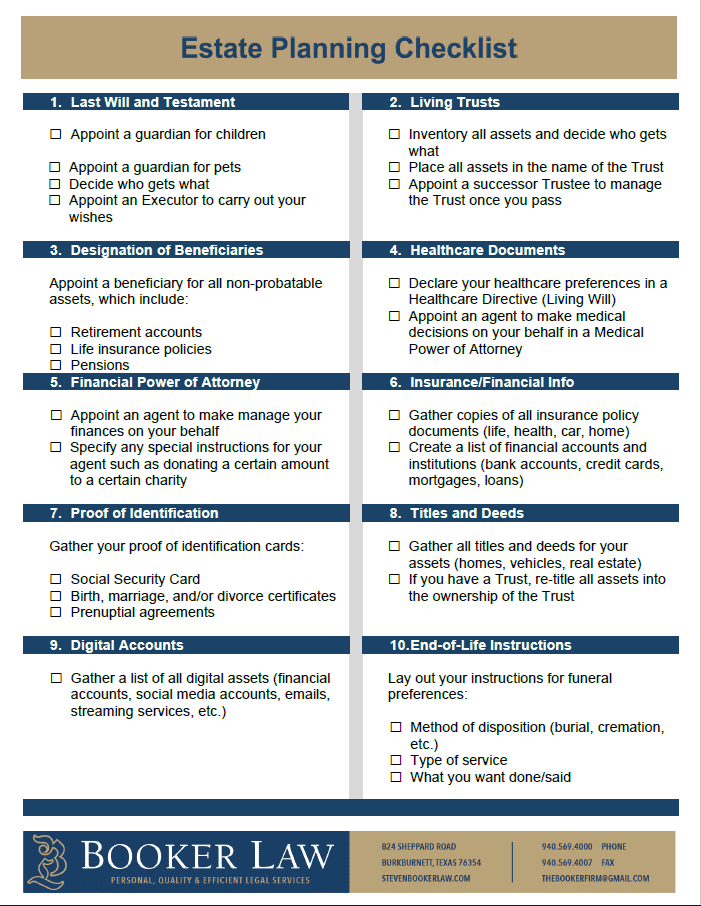
This organized approach to estate management covers essential topics such as wills, trusts, power of attorney, and healthcare directives. Further exploration of these key components will provide a deeper understanding of their roles and importance in comprehensive estate management.
Key Components of an Estate Plan
A comprehensive estate plan requires careful consideration of several key components. Each element plays a vital role in ensuring a smooth transfer of assets and the fulfillment of one’s wishes.
1. Last Will and Testament: This legal document outlines the distribution of assets after death. It designates beneficiaries and appoints an executor to manage the estate.
2. Trusts: These legal arrangements allow for asset management and distribution under specific terms. They offer benefits such as probate avoidance and asset protection.
3. Durable Power of Attorney: This document authorizes a designated individual to manage financial and legal matters on behalf of another person if they become incapacitated.
4. Healthcare Power of Attorney (or Advance Healthcare Directive): This document designates an individual to make healthcare decisions on behalf of another person if they are unable to do so themselves.
5. Living Will (or Advance Medical Directive): This document outlines specific healthcare preferences, such as end-of-life care decisions.
6. Beneficiary Designations: Properly designating beneficiaries for retirement accounts, life insurance policies, and other assets ensures efficient transfer of these assets outside of probate.
7. Inventory of Assets and Liabilities: A detailed record of assets, including real estate, investments, and personal property, as well as outstanding debts, facilitates a clear understanding of the estate’s composition.
Careful planning and documentation of these elements are essential for a well-structured estate plan, providing clarity and minimizing potential complications during a challenging period. Addressing each component thoroughly ensures one’s wishes are respected and their legacy preserved.
How to Create an Estate Planning Guide Template
Developing a structured template provides a valuable tool for organizing essential information and decisions related to estate planning. A methodical approach ensures comprehensive coverage of key elements and facilitates a smoother process.
1: Inventory Assets and Liabilities: Begin by compiling a detailed record of all assets, including real estate, financial accounts, personal property, and business interests. Simultaneously, document all liabilities, such as mortgages, loans, and outstanding debts. This comprehensive inventory forms the foundation of the plan.
2: Define Objectives: Articulate specific goals for the estate plan. These may include distributing assets to beneficiaries, minimizing tax burdens, providing for charitable giving, or establishing trusts for specific purposes. Clearly defined objectives guide subsequent decisions.
3: Designate Beneficiaries: Identify intended recipients of assets and clearly specify their respective shares. Consider contingent beneficiaries in case a primary beneficiary predeceases the individual creating the plan. Accurate beneficiary designations are crucial for efficient asset transfer.
4: Choose an Executor: Select a trustworthy individual or institution to administer the estate and execute the terms of the will. The executor’s responsibilities include managing assets, paying debts, and distributing inheritances.
5: Consider Guardianship: If minor children are involved, designate a guardian to care for them in the event of both parents’ incapacitation or death. This crucial decision ensures their well-being and future.
6: Explore Trust Options: Evaluate the potential benefits of establishing trusts for specific purposes, such as asset protection, probate avoidance, or managing inheritances for beneficiaries. Different trust types cater to various needs.
7: Draft Essential Documents: Engage legal counsel to draft or review essential documents, including a will, power of attorney, and healthcare directives. Professional guidance ensures legal compliance and accuracy.
8: Regularly Review and Update: Life circumstances and financial situations can change. Regularly review and update the estate plan to reflect these changes, ensuring it remains aligned with current objectives and needs.
A well-structured framework incorporates these key elements, providing a comprehensive approach to managing one’s affairs and ensuring a smooth transition of assets according to their wishes. This organized approach simplifies complex decisions and provides peace of mind.
A well-defined framework for managing one’s legacy offers invaluable structure and clarity. From asset inventory and beneficiary designations to the creation of essential legal documents, each component plays a critical role in ensuring wishes are respected and the transfer of wealth is executed smoothly. Utilizing such a structure minimizes potential complications and provides peace of mind for both the individual and their loved ones.
Proactive engagement with the process empowers individuals to take control of their future, providing a lasting legacy for generations to come. Timely and thoughtful preparation ensures a seamless transition and safeguards the interests of those left behind, demonstrating foresight and responsible stewardship.