Utilizing a standardized format offers several advantages. It helps interviewers gather comparable data across all candidates, facilitating more informed decision-making. A consistent approach also improves the candidate experience by ensuring equitable treatment and clear expectations. Furthermore, it can streamline the evaluation process and reduce the time required for candidate selection. Finally, a well-defined framework can protect organizations from legal challenges by demonstrating a fair and consistent hiring practice.
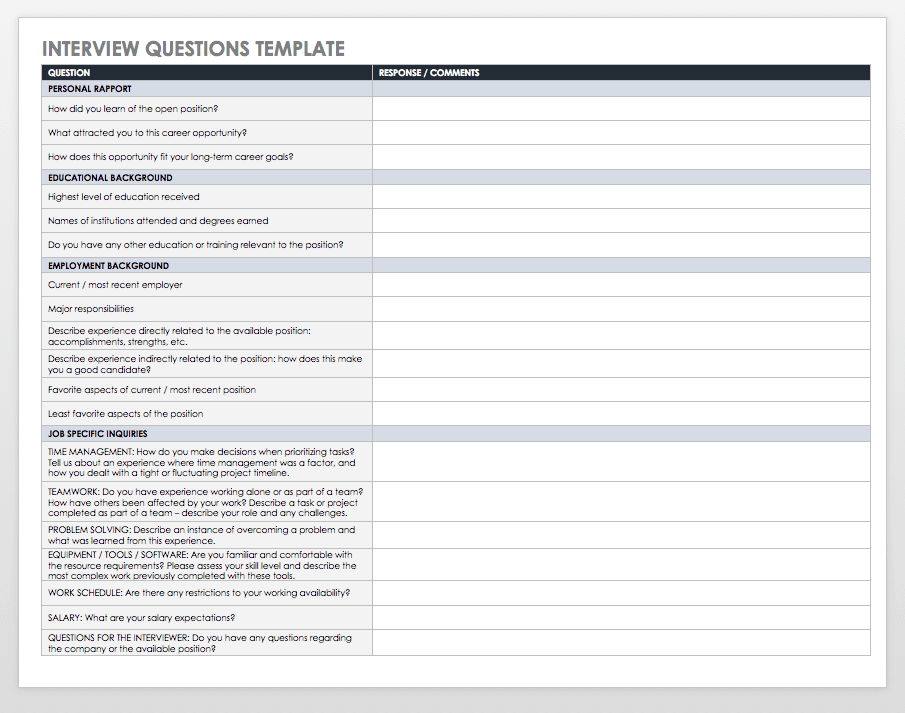
This foundational understanding of a standardized interview format sets the stage for a deeper exploration of its various components, creation strategies, and practical implementation techniques. The following sections will delve into these aspects, providing readers with the knowledge and resources necessary to develop and utilize these valuable tools effectively.
Key Components of a Standardized Interview Format
Effective standardized interview formats share several core components that contribute to their efficacy and ensure consistent, objective evaluations.
1. Introduction: A concise, welcoming introduction sets the tone for the interview and clarifies the purpose and expected duration.
2. Job-Related Questions: Questions should directly assess a candidate’s qualifications and skills relevant to the specific job requirements. Behavioral, situational, and technical questions are common types.
3. Standardized Scoring Rubrics: Predefined rating scales offer consistent evaluation criteria, helping interviewers objectively assess candidate responses against established benchmarks.
4. Note-Taking Sections: Designated space for recording observations and candidate responses allows for detailed documentation and later review.
5. Legal Considerations: Formats should adhere to legal guidelines, avoiding discriminatory questions and ensuring compliance with relevant regulations.
6. Candidate Information Section: A dedicated area to capture essential candidate details, such as contact information and resume highlights, streamlines record-keeping.
7. Closing and Next Steps: Clear communication about the next steps in the hiring process provides candidates with a positive and professional experience.
These elements work together to create a comprehensive and effective tool, enabling organizations to conduct consistent, objective, and legally compliant interviews that contribute to successful hiring outcomes.
How to Create a Structured Interview Guide Template
Developing a robust structured interview guide template requires careful planning and consideration of the specific job requirements and organizational needs. The following steps outline a practical approach to creating a template that promotes consistency, objectivity, and legal compliance.
1. Define the Job Requirements: Thoroughly analyze the target role, identifying essential skills, experience, and qualifications necessary for success. This analysis forms the foundation for relevant interview questions.
2. Choose Appropriate Question Types: Select question types that effectively assess the identified competencies. Behavioral questions explore past performance, situational questions gauge responses to hypothetical scenarios, and technical questions evaluate specialized knowledge.
3. Develop Standardized Questions: Craft clear, concise, and job-related questions that elicit specific and measurable responses. Avoid ambiguous or leading questions.
4. Create a Scoring Rubric: Develop a standardized scoring system to evaluate candidate responses objectively. Define clear criteria for each rating level, ensuring consistency across interviewers.
5. Design the Template Layout: Structure the template logically, incorporating sections for candidate information, interview questions, scoring rubrics, and note-taking space. Ensure a professional and easy-to-use format.
6. Review and Refine: Solicit feedback from stakeholders, including hiring managers and legal counsel, to refine the template and ensure its effectiveness and compliance.
7. Pilot Test the Template: Conduct pilot interviews to evaluate the templates practicality and identify any areas for improvement. Refine the template based on feedback and observations.
A well-designed template provides a framework for conducting consistent and effective interviews, contributing significantly to successful talent acquisition. This structured approach promotes equitable assessment, reduces bias, and supports data-driven hiring decisions.
Standardized interview formats offer a robust framework for conducting effective and objective candidate assessments. From ensuring consistency and legal compliance to streamlining the evaluation process, the benefits are substantial. Key components such as pre-defined questions, standardized scoring rubrics, and designated note-taking sections contribute to a comprehensive and structured approach. Careful planning and development, including a thorough job analysis and selection of appropriate question types, are crucial for creating a high-quality template. Review, refinement, and pilot testing further enhance the template’s effectiveness and practicality.
Organizations seeking to improve their hiring processes should prioritize the development and implementation of these structured tools. The use of standardized interview guides represents a shift towards data-driven decision-making in talent acquisition, promoting fairness, reducing bias, and ultimately contributing to a more effective and successful recruitment strategy.



