Using such a framework promotes a cohesive brand identity and improves user experience by offering a predictable and intuitive navigation structure. It streamlines the design process, reduces development time, and minimizes inconsistencies that might otherwise require costly revisions. Ultimately, it ensures a professional and polished online presence, contributing to improved user engagement and brand recognition.
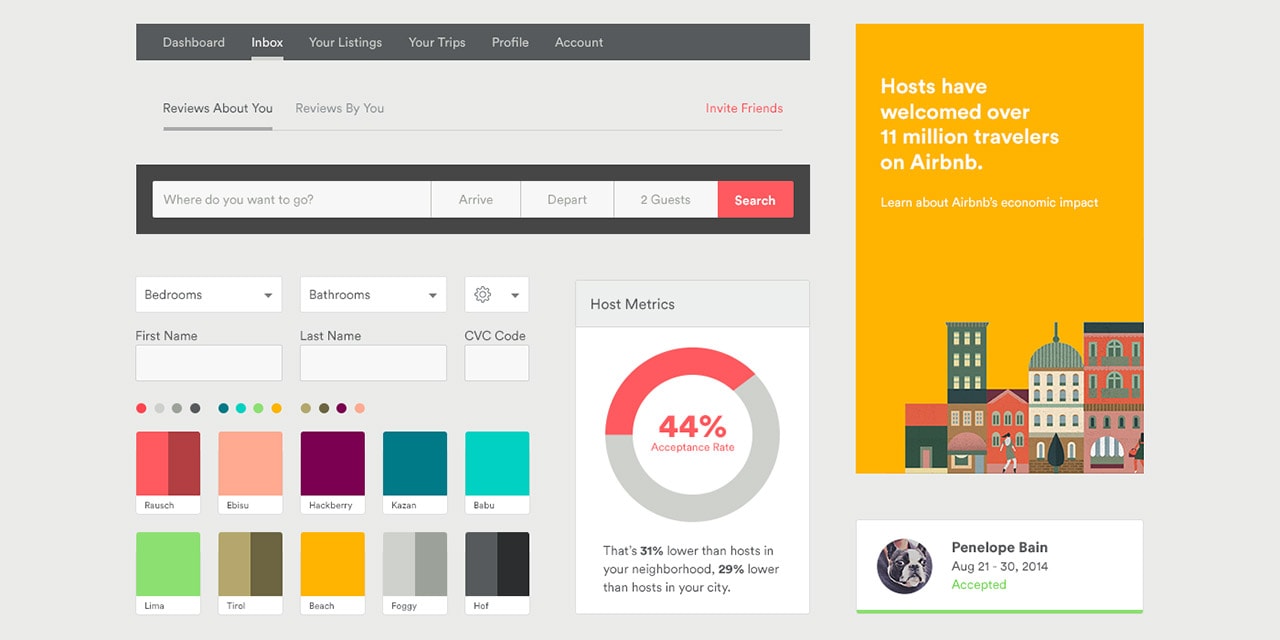
The following sections delve into the core components and practical applications of establishing a comprehensive framework for website design, offering insights into best practices and common considerations.
Key Components of a Web Design Framework
A robust framework for website design comprises several key components, each contributing to the overall consistency and effectiveness of the online presence.
1. Typography: This section specifies font families, sizes, weights, and line heights for headings, body text, and other textual elements. Clear typographic guidelines ensure readability and reinforce brand identity.
2. Color Palette: A defined color palette dictates the primary, secondary, and accent colors used throughout the website. This ensures visual harmony and reinforces brand recognition.
3. Imagery: Guidelines for image usage cover aspects like image style, resolution, and file formats. Consistent imagery contributes to a professional and polished look.
4. Layout & Grid System: Specifications for page layout, grid systems, and spacing ensure consistent placement of elements and contribute to a predictable user experience.
5. Navigation: Navigation guidelines address menu structures, labeling conventions, and interactive behaviors, ensuring intuitive and user-friendly navigation across the website.
6. Forms & Interactive Elements: Styling guidelines for forms, buttons, and other interactive elements maintain a consistent user interface and ensure usability.
7. Coding Practices: Standards for code formatting, commenting, and file organization ensure maintainability and facilitate collaboration among developers.
8. Accessibility: Considerations for accessibility ensure the website is usable by individuals with disabilities, adhering to guidelines like WCAG.
Adherence to these components contributes significantly to a unified and effective online presence, promoting brand consistency, enhancing user experience, and streamlining the development process.
How to Create a Web Page Style Guide
Creating a comprehensive style guide requires a methodical approach, ensuring all essential design and technical elements are addressed.
1. Define Brand Identity: Begin by clearly defining the brand’s personality, values, and target audience. This provides the foundation for all subsequent design decisions within the style guide.
2. Establish Typography Guidelines: Select font families, sizes, and weights for various text elements, ensuring readability and consistency across the website. Specify line heights, letter spacing, and other typographic details.
3. Develop a Color Palette: Choose primary, secondary, and accent colors that align with the brand identity. Document hex codes and usage guidelines for each color to maintain visual harmony.
4. Define Image Standards: Specify preferred image styles, resolutions, and file formats. Include guidelines for image usage, ensuring consistency and visual appeal.
5. Create Layout Specifications: Establish guidelines for page layouts, grid systems, and spacing. Define responsive design behaviors to ensure optimal display across different devices.
6. Outline Navigation Conventions: Specify menu structures, labeling conventions, and interactive behaviors for navigation elements. Ensure intuitive and user-friendly navigation across the site.
7. Detail Component Styles: Provide specific styling guidelines for common UI components like buttons, forms, and interactive elements. Maintain a consistent user interface and ensure usability.
8. Document Code Standards: Establish coding conventions for HTML, CSS, and JavaScript. This ensures maintainability, readability, and facilitates collaboration among developers.
9. Incorporate Accessibility Guidelines: Adhere to accessibility standards like WCAG to ensure the website is inclusive and usable by individuals with disabilities.
A well-defined style guide ensures consistency, streamlines development, and contributes to a positive user experience. Regular review and updates keep the guide relevant and aligned with evolving design trends and technical advancements.
A standardized framework for web page design, encompassing visual elements like typography and color palettes, alongside technical specifications for code and accessibility, is paramount for establishing a consistent and effective online presence. Such a document serves as a blueprint, guiding design and development decisions, promoting brand cohesion, and ensuring a user-friendly experience. It streamlines workflows, reduces development time, and minimizes inconsistencies, ultimately contributing to a polished and professional digital representation.
Maintaining a comprehensive and up-to-date design framework is an ongoing investment in the long-term success of any web project. Consistent application of these guidelines ensures a unified brand identity, enhances user satisfaction, and facilitates future development, solidifying the foundation for a robust and scalable online presence. Adopting and adhering to a structured approach to web design offers significant advantages, contributing to a more efficient, effective, and engaging online experience for all stakeholders.